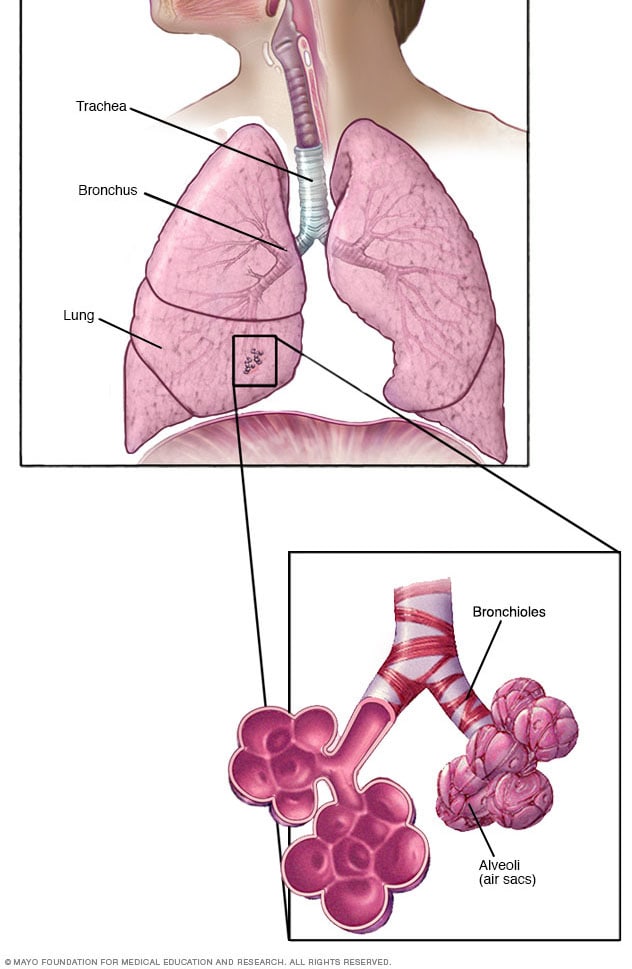
Eating a balanced diet is an important part of good health. The food we eat supplies the nutrient required to build and repair the body, and to provide it with energy. Most of our nutrition consists of three food types-Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats- but vitamin and minerals are also needed in tiny amounts. Water and dietary fibre are other key components. To remain healthy, a person should eat a variety of food in the correct proportion. Carbohydrates, the body's main source of energy, come in two forms- complex carbohydrates and sweet-tasting sugars.
FATS AND OILS
 |
Rich in Fats and Oil |
Although fats and oils supply vitamins and are essential to the functioning of the body, they should be consumed in moderation. Plant oils, such as olive oil,contain unsaturated fatty acids(as do oily fish),which are good for health. However, saturated fatty acids, contained in many animals foods and added to processed foods, can clog arteries.
PROTEINS AND DAIRY FOODS
 |
| Rich in Protein and Dairy food |
About 15 percent of our diet should include proteins needed for growth and repair.Foods rich in proteins include nuts, beans, eggs,fish, meat. Red meat is also rich in saturated fat, harmful to health if eaten in excess. Dairy foods, such as milk and cheese, supply the bone- building mineral calcium and some proteins, but can also be high in fats.
SUGARS
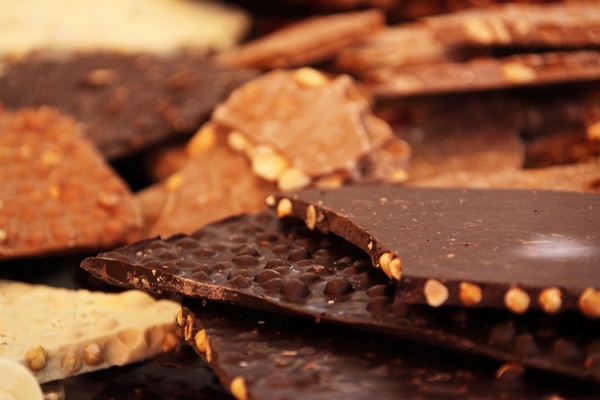 |
Rich in Sugar |
Foods such as sweets, cakes, and biscuits should be eaten sparingly because they contain lots of added sugar. Eating large amount of sugar gives the body sudden bursts of energy rather than the constant stream it obtains from complex carbohydrates. Sugar that is excess to requirement is stored as fat, causing a person to put on weight.
FRUITS AND VEGETABLES
 |
Rich in Vitamins and Minerals |
Fruit is a good source of water, fibre and vitamins, and the natural sugars that give us a burst of energy. Many also supply antioxidants, which can reduce the risk of diseases. Vegetables contain vitamins and minerals and are a good source of fibre. Nutritionists recommend we eat at least five portion of fruit and vegetables daily.
COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES
 |
Rich in Carbohydrates |