BODY SYSTEMS
BODY SYSTEMS
The body's trillions of cells are highly organised .Cells of the same type are grouped together in tissues. Two or more types of tissues are used to build organs that perform specific role. Linked organs from different system that each carry out an essential job, such as digestion. There are 12 body systems that cooperate and interact with each other to form the human body. The organs six systems are the integumental (skin), skeletal(bones) , muscular , endocrine (hormones) ,immune (defence), and reproductive system.
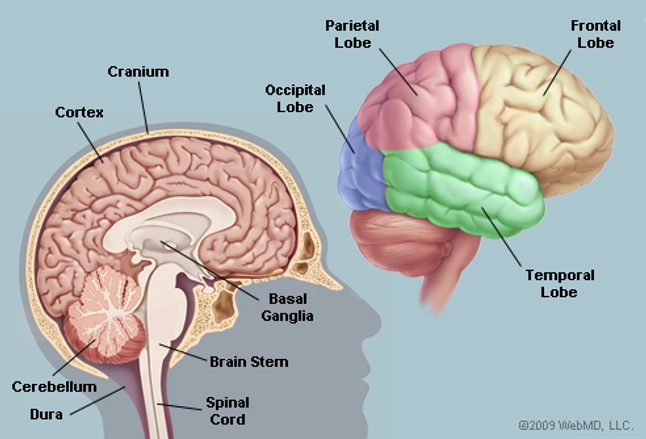
BRAIN
The brain is the centre of the nervous system, which is responsible for controlling body activities . It is dominated by the folded cerebrum that enables us to feel,think and remember , and instructs the body to move. Other brain parts are the cerebellum, tucked under the cerebrum, and the brain stem , which automatically controls breathing and heart rate and links the brain to the spinal cord.
SPINAL CORD
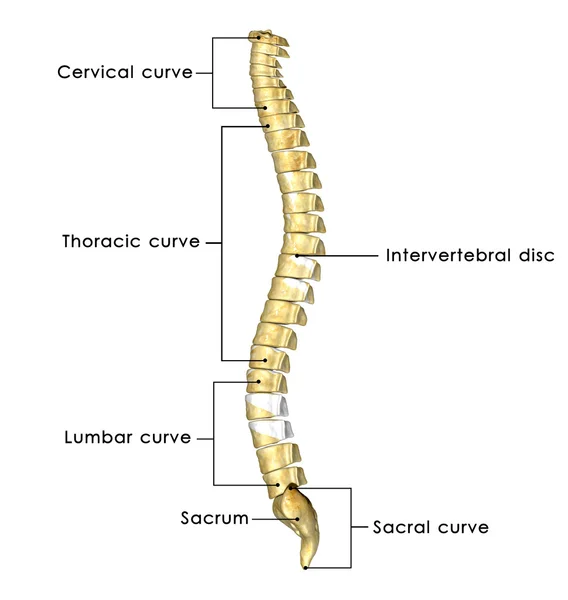
An extension of the brain that runs down the back , the spinal cord relays signals between brain and body through the spinal nerves connected to it . It also controls many of the body's automatic reflex action ,such as pulling the hand back if it touches something sharp. together the brain , spinal cord , nervous form the nervous system .
HEART
The cardiovascular system moves blood around the body to deliver oxygen and food to all the body's cells , and to remove their wastes.located between the lungs , the heart is the centre of this system - a hollow , muscular pump that contracts without tiring more than 70 times a minute to force the blood around the body along blood vessels.
SPLEEN

The spleen is part of the lymphatic system , the body's drainage network . it contains white blood cells , which fight infection by destroying bacteria , and also removes worn - out red blood cells from the blood .
LUNGS

The respiratory system consists of two lungs and the air passes that carry air from the outside . each lungs contain a network of branching tubes that end in millions of tiny air bags. it is from these bags that oxygen in the air passes into the bloodstream. it is carried to all body cells where it is used to release life giving energy from food .
LIVER

The largest internal organ , the liver controls the composition of the blood , processing nutrients newly absorbed from the small intestine .
PANCREAS

The pancreas releases chemicals called enzymes into the small intestine to aid digestion , and hormones(chemical messengers) into the blood to control level of glucose -the body's main fuel in the blood.
STOMACH

This muscular expands as it receives and stores food that has been chewed and swallowed . during storage the stomach's walls churn food into a part-digested "soup", which is released into the small intestine .
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM

The body needs nutrients for energy , growth , and repair . the digestive system breaks down food to release these essential nutrients . the system consists of the mouth and teeth , the oesophagus(a muscular tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), the stomach , and the small and large intestines . food is digested using mechanical force, such as chewing , and through chemical digesters called enzymes. nutrients are then absorbed into the blood and carried to the body's cells .
The large intestine turns waste into faeces (poo) and pushes them out of the body .
The small intestine is a long tube in which most digestion and absorption occurs .
URINARY SYSTEM

Consisting of the kidneys , ureters , bladder , and urethra , the urinary system makes urine and removes it from the body . the kidneys make urine by removing wastes and excess water and salts from the blood thereby keeping its composition constant . Urine is stored in the bladder and expelled through the urethra at its base.









No comments:
Post a Comment