RESPIRATION
The body's trillion of cells require an uninterrupted supply of oxygen to release the energy they need to stay alive . They get this name by means of a process called respiration . Air containing oxygen is breathed into the body by the respiratory system. Oxygen enters the blood stream through the lungs and carried to body cells . waste carbon dioxide is carried by the blood to the lungs breathed in.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Located in the head , neck, and chest , the respiratory system consists of the lungs , which fill most of the chest , and the air passages - nasal cavity , throat , larynx , trachea , and bronchi - that carry air . this x-ray shows the parts of the respiratory system located in the chest .
1. TRACHEA

Also called the windpipe, this flexible tube carries air between the larynx (voice box) at the base of the throat and the two bronchi that arise at its lower end . up to 20 C shaped rings of cartilage that encircle the trachea hold it open when you breathe in . mucus lining the trachea cleans the incoming air by trapping dirt and germs , a process that began in the nasal cavity .
2. BRONCHIAL TREE

Once inside a lung , each bronchus divides into smaller bronchi that then spilt even further . these , in turn , divide repeatedly to form smaller branches called bronchioles . this arrangement is often called "the bronchial tree" because its structure looks like an upside down tree with the trachea as the trunk , bronchi as branches , and bronchioles as twigs .
3. BRONCHIOLES AND ALVEOLI
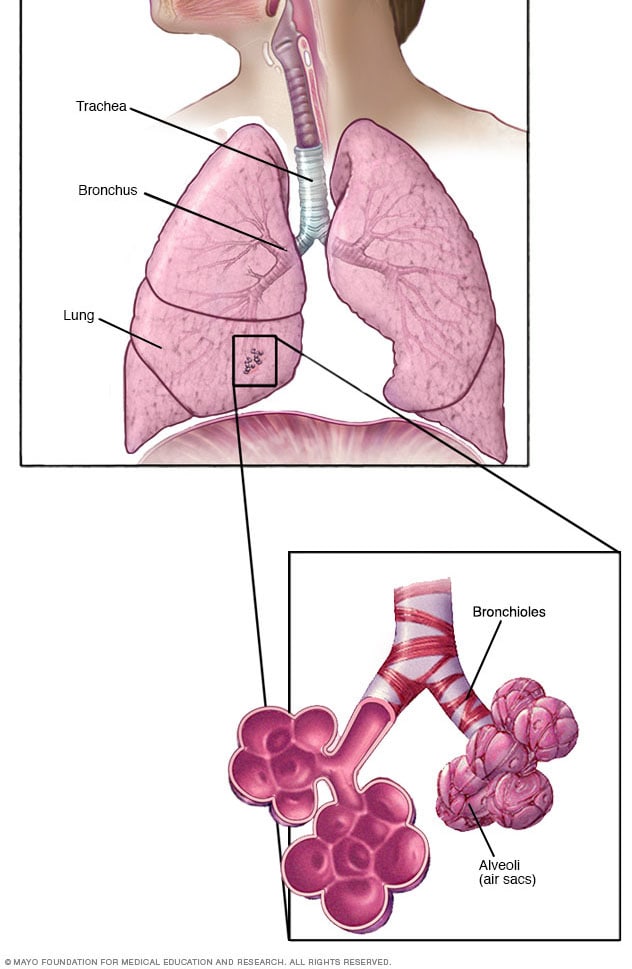
The narrowest bronchioles end in 300 million air filled bags called alveoli that fill most of the lungs and are surrounded by blood capillaries . oxygen passes through the wall of each alveolus into the bloodstream in exchange for carbon dioxide , which moves in the opposite direction . the alveoli provide a large surface across which this exchange take place efficiently .
4. DIAPHRAGM

Situated just below the lungs, the diaphragm plays a key role in breathing . when breathing in, the diaphragm contracts and flattens as muscles pull the ribs upwards and outwards . this increases the space in the chest so that air is sucked into the lungs . when breathing out the relaxed diaphragm is pushed upwards , and the ribs move downwards and inwards , squeezing air from the lungs .
IMPORTANT POINTS
The trachea carries air to and from the lungs .
Twelve pairs of ribs form the ribcage , which protects the lungs and aids breathing
The right bronchus branches from the trachea and divides repeatedly inside the right lung
Muscles between the ribs move the ribcage , which help to pull air into the lungs .
Branches o the smallest bronchioles reach the deepest parts of the lung
The diaphragm is a domed sheet of music that separates chest from abdomen .




No comments:
Post a Comment